| |

|

|
F O U R - S T R O K E C Y C L E
O T T O C Y C L E
|
V 1.0e (18.08.1998)

Fig 1: Nicolaus Adam Otto
|
Nicolaus Adam Otto (Fig 1) the inventor of the four-stroke cycle was born on 14th June 1831 in Holzhausen (Germany).
In 1862 he began first experiments with four-strokes engines. Together with Eugen Langen he founded the first engine company - "N.A.Otto & Cie". Then they improved the atmospheric gas engine (Fig. 2) and in 1867 they won a gold medal at the Paris Exposition. One of the first four-stroke engines is shown in Fig. 3. A working diagram of this engine is shown in Fig. 4. It corresponds to the today's engines. He died on 26th January 1891 in Cologne.
|
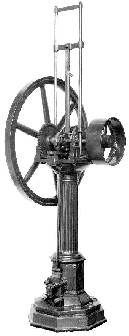
Fig 2: atmospheric gas engine- about 1866/67
|
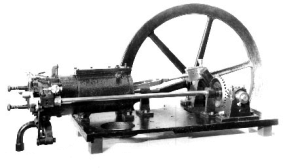
Fig 3: four-stroke cycle engine 1876
|
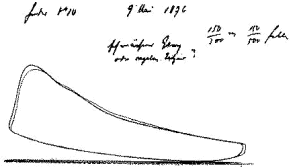
Fig 4: working diagram : 9th May 1876
|
(2) The Parts of the Engine |
|
| The figure at the right shows the main parts of a simple four-stroke cycle engine. These are: the Intake Valve (IV), the Exhaust Valve (EV), the Piston (P), the Piston Rings (PR), the Combustion Chamber (CC), the Connection Rod (CR), the Crank Shaft (CS) and the Spark Plug (SP).
|

the parts of a simple engine
|
(3) The Cycle - Introduction |
|
A 4-stroke cycle engine carried out four piston strokes during one combustion cycle - Intake Stroke, Compression Stroke, Power Stroke and Exhaust Stroke.
During the intake stroke the intake valve is opened and the piston moves toward the crank shaft. The movement of the piston creates a negativ pressure in the combustion chamber. The air/fuel mixture is sucked into the chamber. If the Bottom Dead Center (BDC) is reached the intake valve is closed and the piston moves upwards (compression stroke). The air/fuel mixture is compressed. A short period before the Top Dead Center (TDC) is reached the spark plug ignites the air/fuel mixture. Temperature and the pressure into the combustion chamber increased rapidly. The hight pressure drives the piston downward (power stroke). At the end of the power stroke - at the BDC - the exhaust valve is opened. The piston is moved upward and the gases in the combustion chamber will be pushed through the exhaust valve (exhaust stroke).
(4)The Cycle - The Four Strokes |
|
If you have the ability to measure the pressure in the combustion chamber and its volume during all four strokes you get a diagram like Fig. 6 (p-V diagram). It represents the state of the gas in the chamber.
|
The figures of the state of a simplified engine as so as the corresponding p-V diagrams were taken form the Online Animation of a Four-Stroke Cycle site. The single point shown in the p-V diagram represents the common state. The color of the combustion chamber indicates the temperaure (red: hot; blue: cold).
|
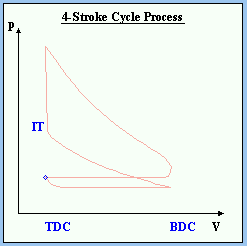
Bild 6: p-V diagram
|
INTAKE STROKE
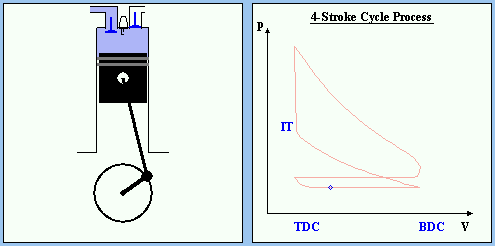
Fig 7: INTAKE STROKE
|
The piston moves down the cylinder and the pressure will drop (negative pressure). The intake valve is opend. Because of the low pressure the air/fuel mixtures is sucked into the cylinder.
|
COMPRESSION STROKE
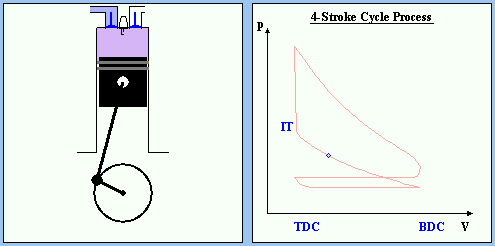
COMPRESSION STROKE
|
At Bottom Dead Center (BDC) the cylinder is at its maximum volume and the intake valve is closed. Now the piston moves backward the Top Dead Center (TDC) and compresses the air/fuel mixtures. The pressure is increased and the volume is decreased. The necessary work for the compression increases the internal energy of the mixtures - the temperature is increased. Because of the fast compression only a small part of the energy is transfered to the environment.
|
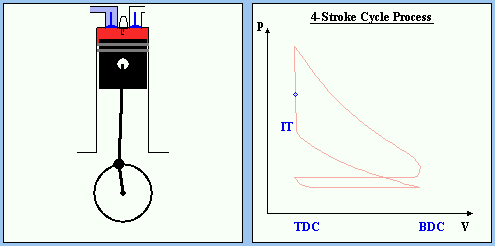
Fig 9: IGNITION
|
Near the end of the compression stroke, the ignition starts the combustion and the mixture burnes very rapidly.
The expanding gas creates a high preasures against the top of the piston. The resulting force drives the piston downward in the cylinder.
|
POWER STROKE
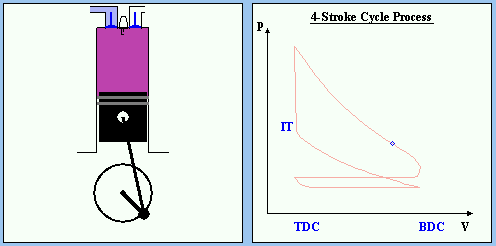
Fig 10: POWER STROKE
|
The force drives the piston downward to crank shaft (the valves are closed). The volume is increased and the preasure is decreased. No more energy is added and because of this the internal energy of the gas is decreased as so as the temperature.
|
EXHAUST STROKE
|
At BDC the exhaust valve is opend and the piston moves up the cylinder. The pressure drops near the preasure outside the cylinder because of the opened exhaust valve. Exhaust gas leaves the cylinder. The volume is decreased.
|
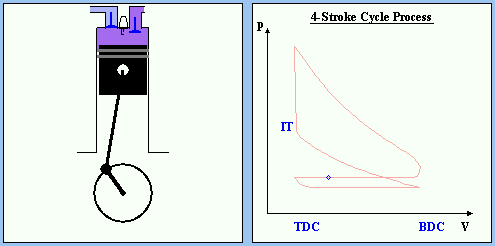
Fig 11: EXHAUST STROKE
|
More information : Links & Literature - Four-Stroke Cycle Engines.






